Général
- Congénitaux, Rares
- Entrainent une stase biliaire
- Clinique: Jaunisse, douleur abdominale, masse abdominale
- Peuvent être associés à une atrésie des voies biliaires
- Risque: Dégénérescence en Cholangiocarcinome
Types (classification de Todani)
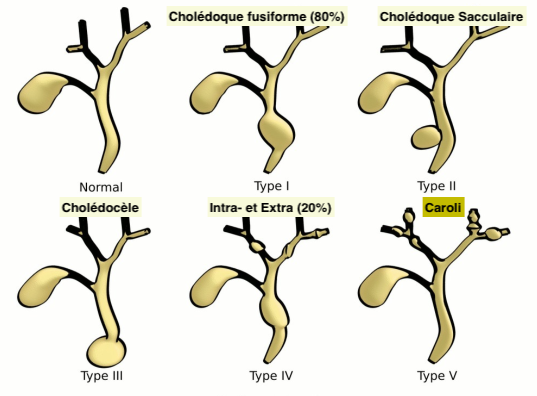
- type I: most common, accounting for 80-90% (this type can present in utero)
- type II: true diverticulum from extrahepatic bile duct
- type III: dilatation of extrahepatic bile duct within the duodenal wall (choledochocoele)
- type IV: next most common
- type V: multiple dilatations/cysts of intrahepatic ducts only (Caroli disease)
Risques
- Les plus fréquents : Type I (80%) et IV (19%) Sont aussi les plus à risque de dégénerescence carcinomateuse
- Résection chirurgicale avec anastomose hépatico-jéjunale
IRM
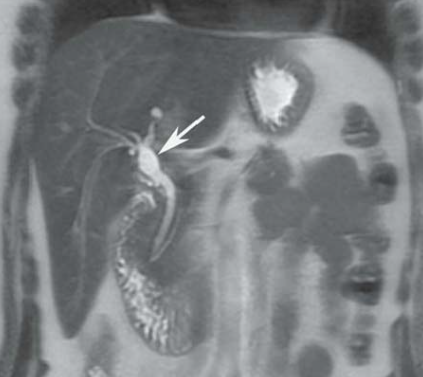
Type I
US Neonatal
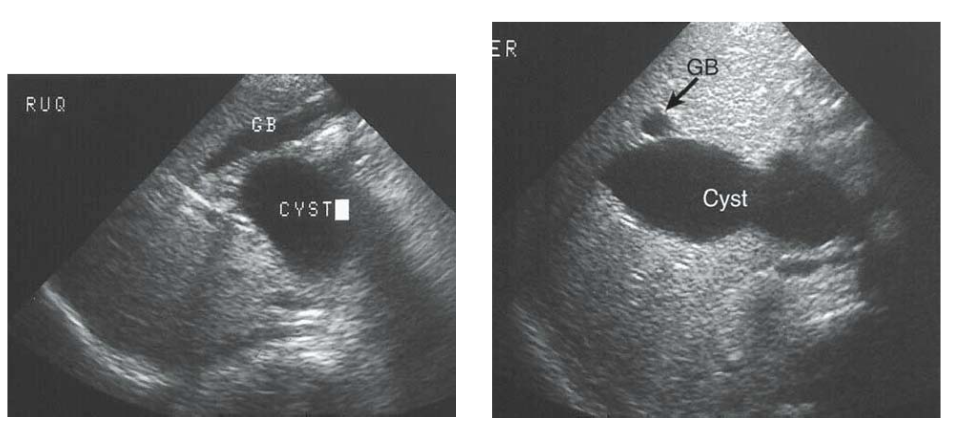
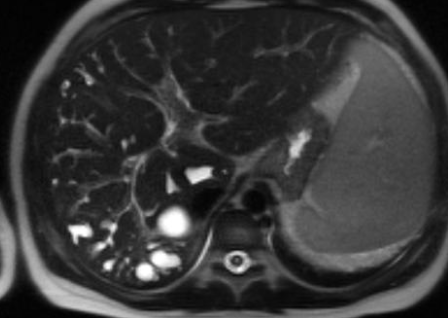
Maladie de Caroli
Général
- Multiples dilatations kystiques des VB intrahépatiques
- Central dot sign parfois
- Todani Type V
- Stase biliaire, surinfections, calculs biliaires
- Risque de Cholangiocarcinome
- Associé à ADPKD, ARPKD, Reins en éponge médullaire
- PAS Confondre avec Syndrome De Caroli = Dilataiton des grands axes biliaires dus à une fibrose hépatique


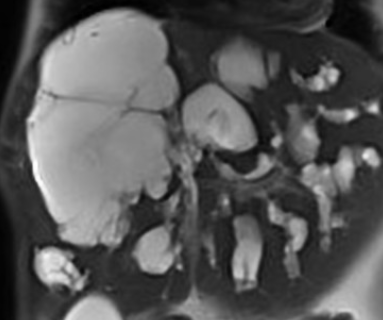
Type I II III IV V Caroli choledoque choledocien cholédocien choledocele